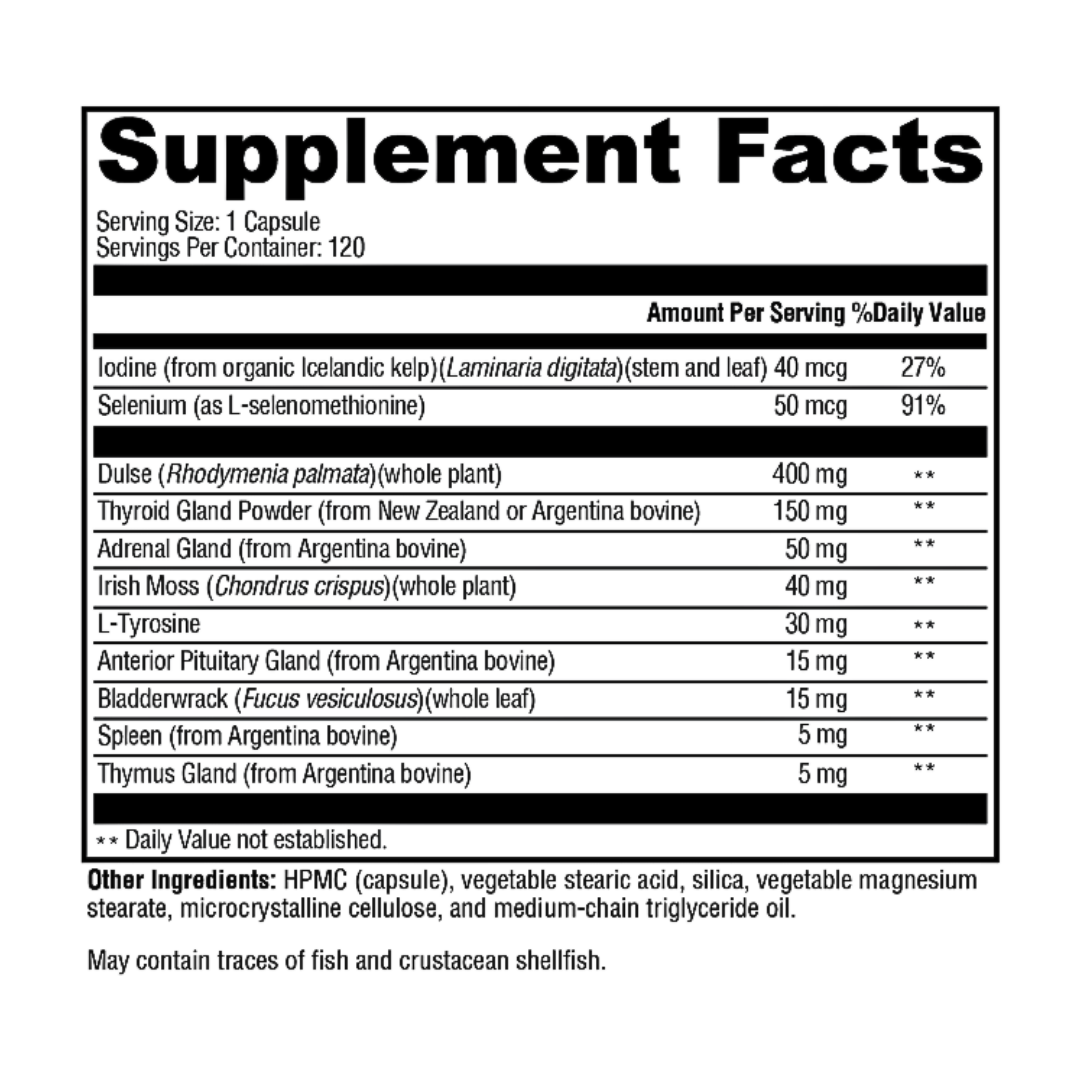
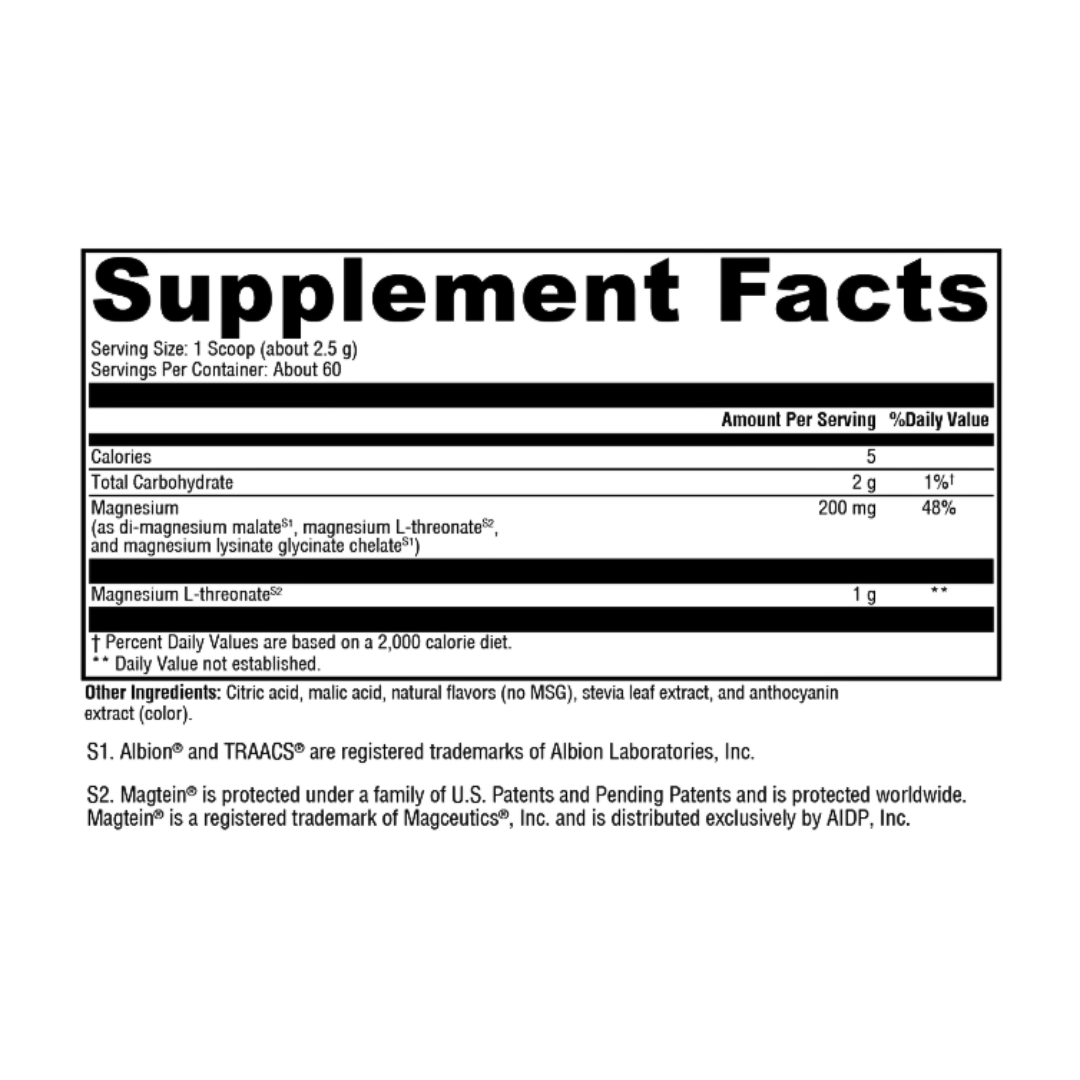
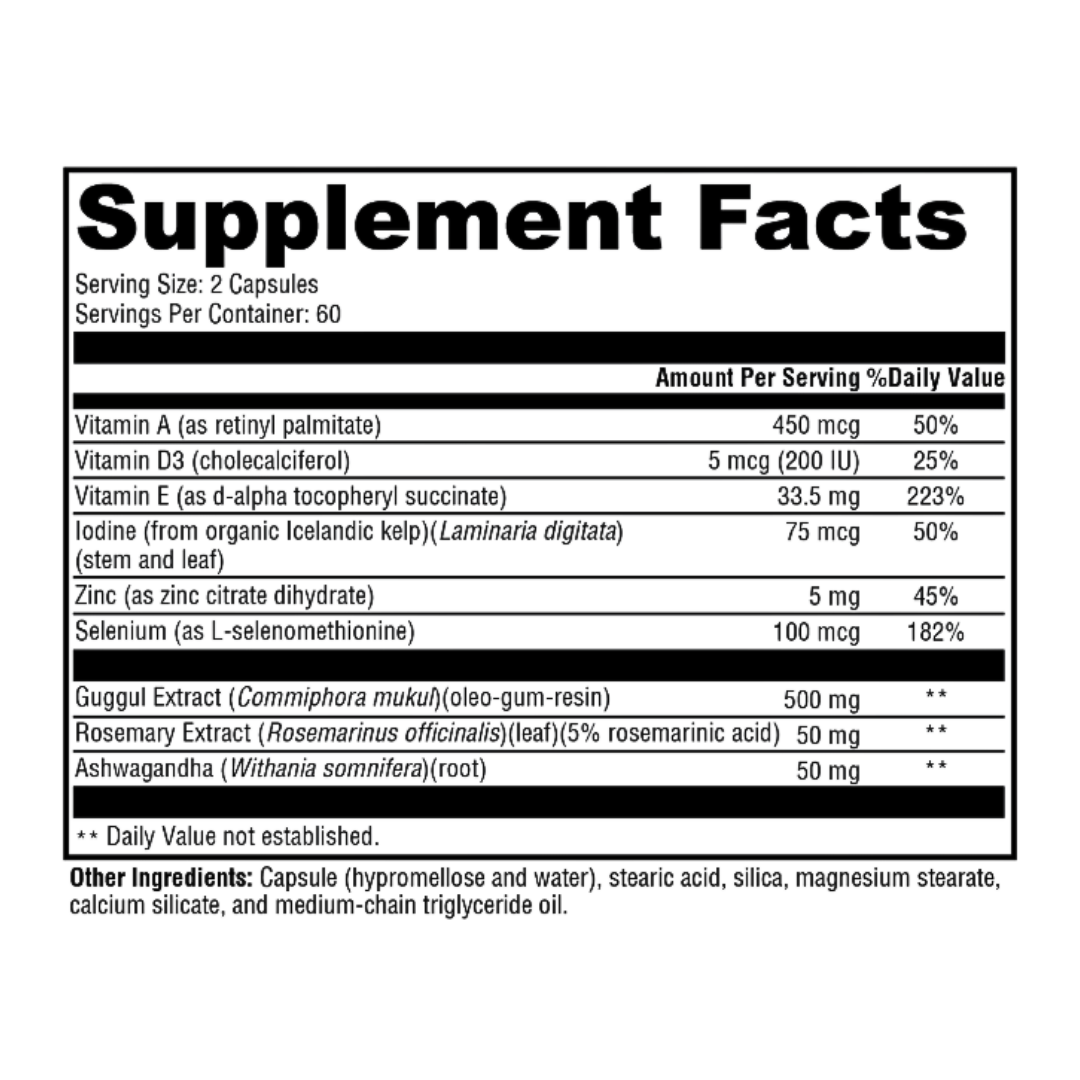
Plant-Powered Formulas
Naturally derived and organic ingredients
Science-Backed Ingredients
Clinically studied and evidence-based
Made in the UNITED STATE
Strict quality standards in every batch
Vegan & Cruelty-Free
No animal ingredients or testing
Pure and Natural PRODUCTS
No artificial additives or fillers
100% Clean
Free from gluten, dairy, sugar, and GMOs
Herbs
Herbs have been used for thousands of years to support natural healing and balance.
At Purety, we continue that tradition, with formulas tested in real clinical practice, crafted for safety, and made to deliver results you can feel.

CLINICALLY TESTED ON REAL PATIENTS
Every formula has been used and trusted in our medical practice, chosen because it made a real difference.
ORGANIC, WILD-CRAFTED, AND CLEAN
Sourced from pure, natural plants. Free from synthetic fillers, GMOs, and common irritants.
VISIBLE SUPPORT, NATURALLY
Herbal remedies work with your body’s natural healing processes, often supporting noticeable improvements within days or weeks.
MADE WITH CARE IN THE USA
Handcrafted in Sedona, Arizona under strict quality and safety standards.

Formulas Developed Through Clinical Experience
Herbs have been used for thousands of years as one of the most trusted forms of natural healing. Across generations and cultures, they have supported the body’s ability to restore balance and health.
At Purety, we continue that tradition through clinical practice. Each formula was created through years of direct patient care, used to address real health concerns and track real outcomes. Every product reflects what has been proven effective through hands-on experience.
EXPLORE OUR BEST SELLERS
FAQ
Are your products organic?
Yes — whenever possible, we use certified organic or wild-crafted ingredients, especially in our herbal formulas. Every product is carefully vetted for purity, potency, and sourcing. While not every supplement carries an organic label (due to patented ingredients or specialized extracts), all products meet the highest standards of quality and bioavailability — physician-grade, with no unnecessary fillers.
Do you test for pesticides?
Yes. All of our herbal formulas and supplements are tested for pesticides by third-party laboratories. We only partner with manufacturers who uphold strict quality standards to ensure that every ingredient is clean, safe, and free from harmful residues.
What is your policy on GMOs?
We are committed to using non-GMO ingredients whenever possible. The majority of our herbal formulas and supplements are formulated without genetically modified organisms. We work exclusively with manufacturers who share our standards for purity, transparency, and clean sourcing.
Do you test for heavy metals?
Yes. All of our herbal formulas and supplements are tested for heavy metals through third-party laboratories. We only work with manufacturers who meet strict safety standards to ensure that every product is clean, safe, and free from harmful contaminants.
Our Story
Where Nature’s Wisdom Meets Clinical Care
We’re Dena and Jonathan Birch — two naturopathic doctors, and believers in a different kind of healthcare. Years ago, we built our practice around a simple truth: healing must honor the whole person — body, mind, and spirit.
Purety grew from that same belief. Our formulas aren’t created in distant labs — they’re shaped by real conversations, real patients, and a commitment to nature’s inherent ability to heal. Every ingredient we choose reflects our philosophy: to find and treat the root cause, to support the body’s natural balance, and to always seek the least invasive, most effective path to wellness.
We believe that true health is multi-dimensional, and so is our approach. By merging medical science with holistic therapies, we create supplements that are not just clean, but purposeful — designed to empower you and your family toward lasting wellness.
If you’ve ever sat in our clinic, you know how seriously we take this work. If you’re new here, you’ll feel it the moment you try our products — the difference that comes from care, intention, and a deep respect for the body’s ability to heal itself.
Welcome to Purety — where holistic health is personal.
With care and intention,
Dena and Jonathan Birch
Trusted by People Who Believe in Natural Healing
Real stories from people who use our products to support natural healing and whole-body wellness.